ISO 22493 pdf download

ISO 22493 pdf download Microbeam analysis — Scanning electron microscopy — Vocabulary
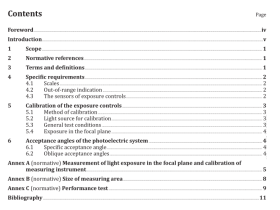
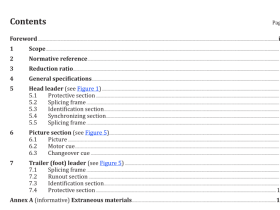
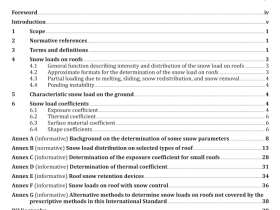
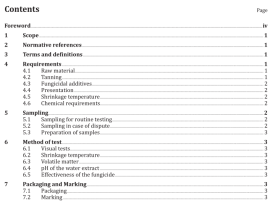
1 Scope
This International Standard defines terms used in the practice of scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It covers both general and specific concepts, classified according to their hierarchy in a systematic order, with those terms that have already been defined in ISO 23833 also included, where appropriate.
This International Standard is applicable to all standardization documents relevant to the practice of SEM. In addition, some clauses of this International Standard are applicable to documents relevant to related fields (e.g. EPMA, AEM, EDS) for the definition of terms which are relevant to such fields.
2 Abbreviated terms
AEM analytical electron microscope/microscopy
BSE (BE) backscattered electron
CPSEM controlled pressure scanning electron microscope/microscopy
CRT cathode ray tube
EBIC electron beam induced current
EBSD electron backscatter/backscattering diffraction
EDS energy-dispersive spectrometer/spectrometry
EPMA electron probe microanalyser/analysis
ESEM environmental scanning electron microscope/microscopy
FWHM full width at half maximum
SE secondary electron
SEM scanning electron microscope/microscopy
VPSEM variable-pressure scanning electron microscope/microscopy
3?Terms?and?definitions?used?in?the?physical?basis?of?SEM
3.1
electron optics
science that deals with the passage of electrons through electrostatic and/or electromagnetic fields
3.1.1
electron source
device that generates electrons necessary for forming an electron beam in the electron optical system
3.1.1.1
energy spread
diversity of energy of electrons
3.1.1.2
effective?source?size
effective dimension of the electron source
3.1.2
electron emission
ejection of electrons from the surface of a material under given excitation conditions
3.1.2.1
field?emission
electron emission caused by the strong electric field on and near the surface of a material
3.1.2.1.1
cold?field?emission
field emission in which the emission process relies purely on the high-strength electrostatic field in a high-vacuum environment with the cathode operating at ambient temperature
3.1.2.1.2
thermal field?emission
Schottky emission
field emission in which the emission process relies on both the elevated temperature of the cathode tip and an applied electric field of high voltage in a high-vacuum environment
3.1.2.2
thermionic emission
electron emission that relies on the use of high temperature to enable electrons in the cathode to overcome the work function energy barrier and escape into the vacuum
3.1.3
electron lens
basic component of an electron optical system, using an electrostatic and/or electromagnetic field to change the trajectories of the electrons passing through it
3.1.3.1
electrostatic lens
electron lens employing an electrostatic field formed by a specific configuration of electrodes
3.1.3.2
electromagnetic lens
electron lens employing an electromagnetic field formed by a specific configuration of electromagnetic coil (or permanent magnet) and pole piece
3.1.4
focusing
aiming the electrons onto a particular point using an electron lens
3.1.5
demagnification
numerical value by which the diameter of the electron beam exiting a lens is reduced in comparison to the diameter of the electron beam entering the lens
3.2
electron scattering
electron deflection and/or its kinetic energy loss as a result of collision(s) with target atom(s) or electron(s)
3.2.1
elastic scattering
electron scattering in which energy and momentum are conserved in the collision system