ISO 15625 pdf download

ISO 15625 pdf download Silk — Electronic test method for defects and evenness of raw silk
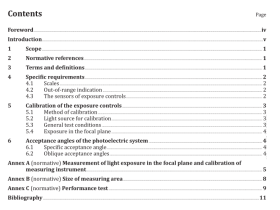
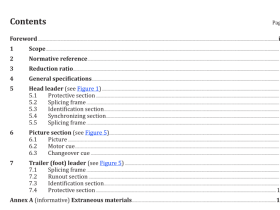
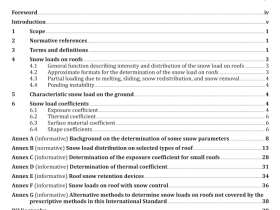
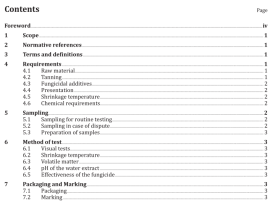
Scope
This International Standard specifies a test method for defects and evenness of raw silk by capacitiveand optical electronic testers.
This International Standard is applicable to raw silk with the yarn size between 13,3 dtex and 76,7 dtexor 12 denier and 69 denier, whether in skein or on cone, soaked or unsoaked.
2 Normative references
The following documents,in whole or in part, are normatively referenced in this document and areindispensable for its application. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undatedreferences, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 139, Textiles — Standard atmospheres for conditioning and testingISO 2060, Textiles – Yarn from packages — Determination of linear density (mass per unit length) by theskein method
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1
raw silk
silk filament yarn formed by conglutinating a number of bombyx mori cocoon baves by reeling machineaccording to a certain reeling technique and quality requirement
3.2
soaked silkraw silk soaked in a formulation of additives according to a technical requirement
3.3
electronic test methodmethod for evaluating the defects and evenness by using capacitive and optical testers
3.4
slub
for the capacitive method, the defect whose length is equal to or greater than 1 mm and whose masssurpasses 80 % of the average mass of the testing sample; for the optical method, the defect whoselength is equal to or greater than 1 mm and whose cross-sectional area surpasses 80 % of the averagecross-sectional area of the testing sample
Note 1 to entry: Slub can be classified into big slub and small slub, which can be referred to A.11
3.5thick place
for the capacitive method, the defect whose length is equal to or greater than 10 mm and whose masssurpasses 35 % to 80 % of the average mass of the testing sample; for the optical method, the defectwhose length is equal to or greater than 10 mm and whose cross-sectional area surpasses 30 % to 80 %of the average cross-sectionalarea of the testing sample
4 Principle
Defects of raw silk, soaked or unsoaked, are evaluated, classified, and counted on the basis of variation of the electric capacity, in case of capacitive sensors, and of the photoelectric effect, in case of optical sensors, when passing through suitable sensors splits. The difference between optical and capacitive sensors in detecting defects of raw silk is shown in Annex B. The evenness of raw silk, soaked or unsoaked, is evaluated and counted on the basis of variation of electric capacity only in capacitive sensors. The measurements are performed on individual yarn.
5 Apparatus
5.1 General The electronic tester for raw silk can be single spindle or multi-spindle, and it comprises the measurement module consisting of capacitive and optical testers, signal processing module, and framework.
5.2 Measurement module.
5.2.1 Capacitive tester, used to test slub, thick place, thin place, SIE, and evenness of raw silk, with no more than 5 % of testing precision and 1 mm of minimum yarn advancement length.